Enhancing Farm Productivity Through Effective Grain Care
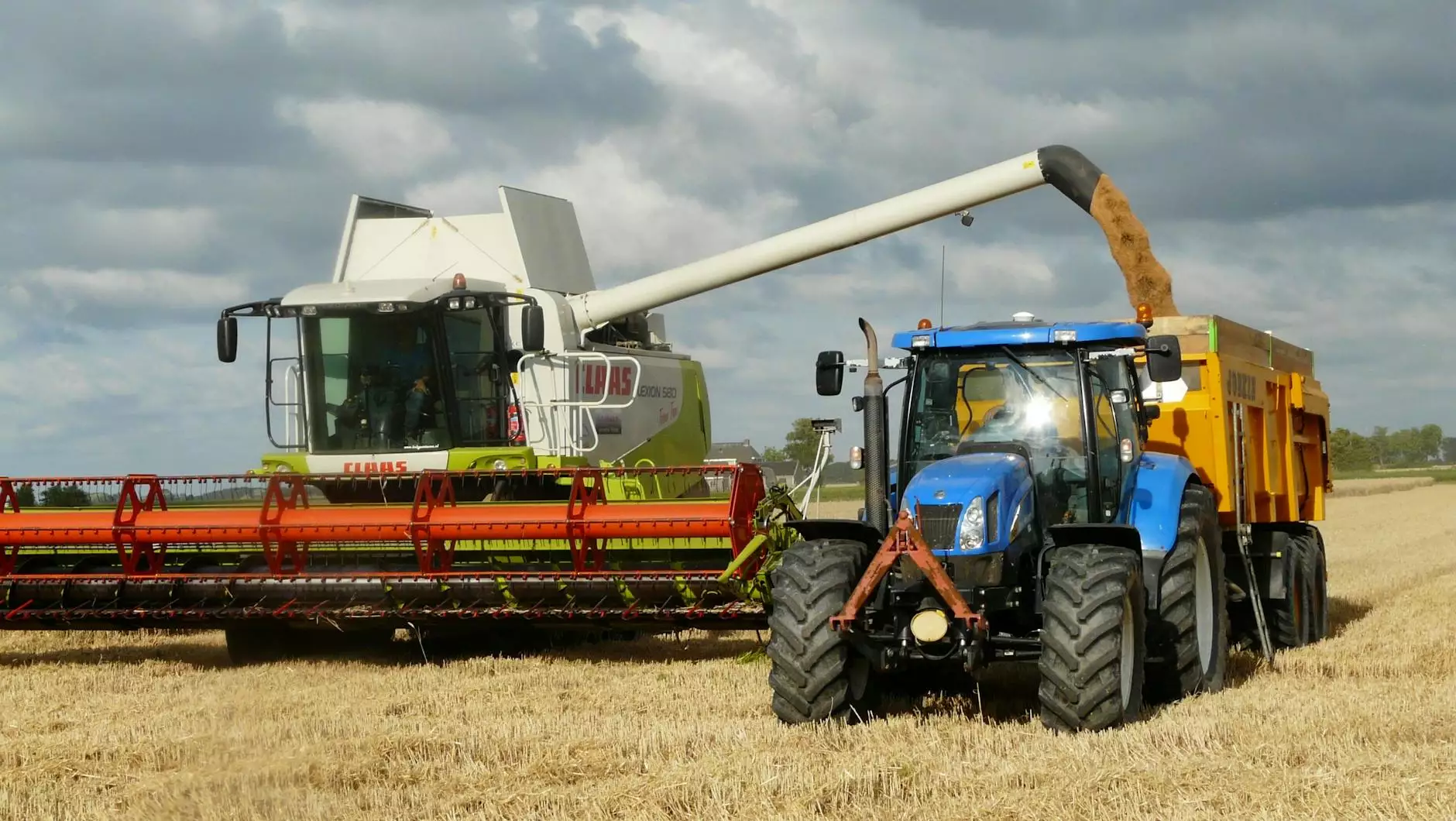

In the realm of agriculture, grain care is a pivotal component that significantly impacts overall farm productivity and profitability. For farmers and agricultural businesses, understanding the nuances of maintaining quality grain through effective care techniques is essential. This article offers an in-depth exploration of the best practices, tools, and strategies for optimal grain care, ensuring that your produce meets market demands while maximizing your operational efficiency.
Understanding the Importance of Grain Care
The grains produced on a farm are not just commodities; they play a critical role in the global supply chain, food security, and the economy. Proper grain care influences quality and yield, impacting everything from household consumption to market pricing. Here are some fundamental aspects to consider:
- Quality Preservation: Good grain care protocols help maintain the quality of grains, preventing spoilage and degradation over time.
- Market Value: High-quality grains fetch better prices on the market, directly correlating to a farmer's profit margins.
- Sustainability: Effective grain care contributes to sustainable farming practices, reducing waste and enhancing resource efficiency.
- Consumer Trust: Reliable grain quality builds consumer trust, fostering long-term relationships between farmers and buyers.
Key Strategies for Optimal Grain Care
To achieve effective grain care, farmers can adopt several strategies that encompass equipment maintenance, environmental controls, and market readiness:
1. Equipment Maintenance and Repair
Farm equipment repair is crucial for ensuring that all machinery operates at peak efficiency. Here are several types of equipment that are essential for grain care:
- Harvesters: Regularly serviced harvesters ensure that the grains are harvested efficiently and with minimal damage.
- Thrashers: Ensure that thrashers are calibrated and maintained to prevent quality loss through grain damage during processing.
- Driers: Properly functioning grain driers control moisture levels, preventing mold and spoilage.
- Storage Equipment: Bins and silos must be inspected for structural integrity and climate control to maintain grain quality.
2. Optimal Storage Conditions
One of the most critical aspects of grain care is ensuring proper storage conditions. Grains are highly vulnerable to pests, moisture, and temperature variations. Here are some essential storage practices:
- Moisture Control: Maintain ideal moisture levels to prevent fungal growth. Use moisture meters to monitor conditions regularly.
- Pest Management: Implement pest control measures using traps and environmentally safe pesticides to reduce infestations.
- Temperature Regulation: Use aeration systems to keep grain cool and at consistent temperatures.
- Regular Inspections: Schedule regular inspections to identify potential issues before they escalate.
3. Innovative Practices in Grain Care
Advancements in technology offer new methods to enhance grain care practices. Consider integrating the following innovative strategies into your farming operations:
- Data Monitoring and Analysis: Utilize sensors and software to collect data on grain conditions, analyzing trends to make informed decisions.
- Drones for Surveillance: Use drones to survey fields and storage facilities for signs of pests or structural issues.
- Automated Systems: Implement automation for drying, sorting, and storing grains, which can minimize labor and improve efficiency.
Best Practices for Grain Handling
Proper handling of grains from harvest to storage is equally essential for maintaining quality and ensuring successful market placements:
1. Safe Harvesting Techniques
Ensure that the grains are harvested at optimal moisture levels to avoid spoilage. Utilize modern harvesting technology to reduce the amount of grain left behind in the field, which can lead to losses.
2. Efficient Transportation
Use clean and well-maintained transport vehicles to ensure that grains are moved safely to storage or market locations. This practice helps to minimize contamination and spoilage during transit.
3. Attention to Detail During Processing
During processing, maintain a clean environment to prevent contamination. Regularly maintain processing equipment to ensure consistent performance.
The Economics of Grain Care
The economics related to grain care must not be overlooked. Here are some cost-related aspects to keep in mind:
- Investment in Equipment: Investing in high-quality, reliable equipment can reduce maintenance costs and increase efficiency.
- Cost of Losses: Understand the financial implications of grain losses due to poor care. This includes losses from spoilage, pest damage, and quality degradation.
- Market Pricing: Stay informed of market trends to position grains competitively, ensuring they meet market standards.
Conclusion: The Future of Grain Care
The future of agriculture hinges on effective grain care practices that embrace technology, efficiency, and sustainability. As farmers continue to face evolving challenges, staying informed about innovative techniques and maintaining diligence in grain management will be vital for survival in the competitive agricultural landscape.
A commitment to grain care not only reflects the dedication of farmers towards their craft but also the essential role they play in feeding the world. By following the best practices outlined in this guide and being adaptive in an ever-changing market, farmers can ensure that their operations thrive while contributing positively to the global food supply chain.
For more information on grain care and farm equipment repair, visit tsgcinc.com, your reliable partner in agricultural excellence.